Chrome plating is a popular and versatile technique that can enhance the appearance and performance of various metal objects. Whether you want to give your car a shiny and sleek look or improve the durability and functionality of your industrial equipment, chrome plating can offer you many benefits. But what exactly is chrome plating, and how does it work? In this blog post, we will provide you with a comprehensive guide to chrome plating, covering its definition, process, purpose, types, and removal methods. By the end of this post, you will have a better understanding of chrome plating and its applications.

What Is Chrome Plating?
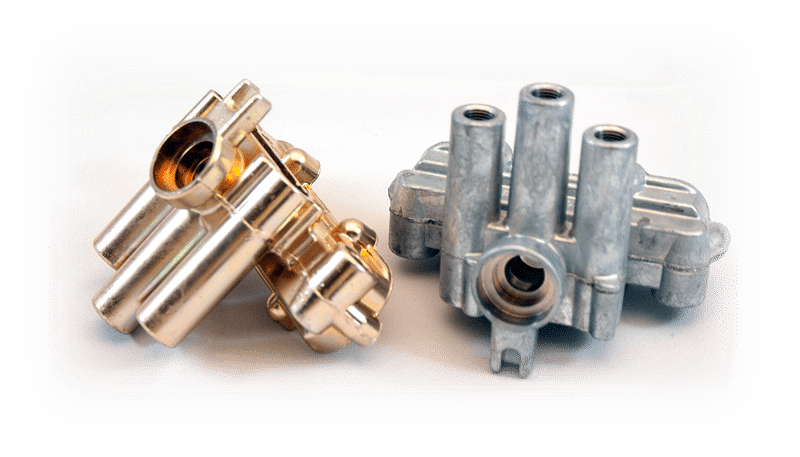
Chrome plating is a technique of applying a thin layer of chromium onto a metal object through an electroplating process. Chrome plating is more than just enhancing the appearance of the object. It also increases the surface hardness and durability, prevents corrosion, and makes the object easier to clean.
Typical Process of Chrome Plating
Chrome plating is a process that coats a metal surface with a thin layer of chromium. There are two main methods of chrome plating: hexavalent chromium and trivalent chromium.
Hexavalent Chromium
This is the traditional method of chrome plating that is mainly used for industrial purposes. It involves using chromium trioxide, which is highly toxic and carcinogenic. The waste produced by the hexavalent chromium bath is dangerous and needs to be treated before disposal.
Trivalent Chromium
This is a newer method of chrome plating that uses chromium sulphate or chromium chloride. It can achieve similar results as hexavalent chromium in some applications and thicknesses. Trivalent chromium is much less harmful than hexavalent chromium. It is an eco-friendly alternative to the conventional chrome plating method. However, Trivalent chromium still requires careful handling and disposal of any waste.
The Steps of Chrome Plating
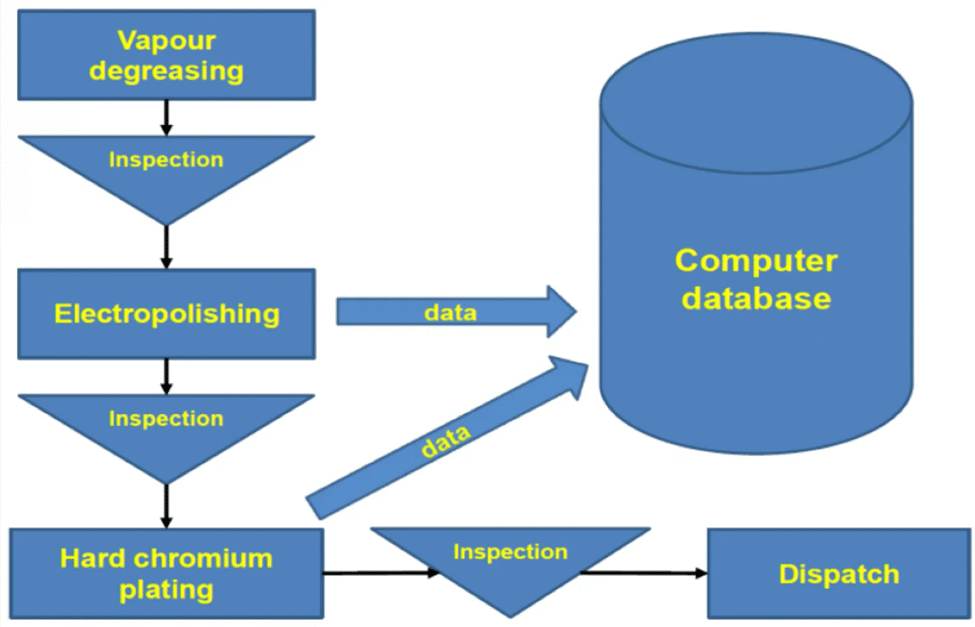
The first step in chrome plating is cleaning and degreasing the metal object to remove all traces of dirt and impurities. The object is then subjected to various pretreatments depending on the type of metal to ensure proper adhesion of the chrome layer. The object is then placed in the chrome plating vat, where it is immersed in an electrolyte solution containing chromic acid and other chemicals. An electric current is passed between two electrodes, one of which is the object to be plated. The current causes chromium atoms to deposit on the surface of the object, forming a thin layer of chrome.
Purpose of Chrome Plating
Chrome plating has several purposes, depending on the type and thickness of the chrome layer. Some of the common purposes are:
– To improve the appearance and aesthetic appeal of the object
– To increase the surface hardness and wear resistance of the object
– To protect the object from corrosion and rust
– To reduce friction and improve lubricity of the object
– To enhance the electrical conductivity or reflectivity of the object
Types of Chrome Plating
There are two types of Chrome Plating:
Decorative Chrome Plating
This type of chrome plating is used to make metal objects look shiny and attractive. It usually involves electroplating a thin layer of chromium over a layer of nickel or copper. The nickel or copper layer provides smoothness, reflectivity, and protection from corrosion.
The thickness of the decorative chrome layer is typically between 0.002mm and 0.02mm. This means that it is not very durable and can wear off easily.
Hard Chrome Plating
This type of chrome plating is used to improve the performance and longevity of metal parts. It usually involves electroplating a thick layer of chromium directly on the metal surface. The thickness of the hard chrome layer is typically between 0.02mm and 0.04mm.
Hard chrome plating offers excellent resistance to wear and corrosion, as well as increased hardness and strength. It also prevents parts from sticking together and enhances their chemical stability, especially against oxidation.

The Difference Between Hard Chrome and Decorative Chrome Plating
The main difference between hard chrome and decorative chrome plating is the thickness of the chrome layer. Hard chrome plating has a much thicker layer than decorative chrome plating, which affects their properties and applications.
Some of the other differences are:
Property: The second difference between hard and decorative chrome plating is how they affect the properties of the metal parts. Hard chrome plating increases the hardness and strength of the metal, making it more resistant to friction, wear, corrosion, and other damage. Decorative chrome plating improves the appearance of the metal, giving it a shiny and smooth surface. It also has some wear resistance, but not as much as hard chrome plating.
Applications: Hard chrome plating is mainly used for industrial purposes, such as improving the performance and durability of machinery parts, tools, and equipment. Decorative chrome plating is mainly used for aesthetic purposes, such as enhancing the appearance and appeal of consumer products.
How to Remove Chrome Plating?
Sometimes, you may need to remove chrome plating from metal objects, either to restore the original finish or to apply a different coating. There are different methods to remove chrome plating, depending on the type and size of the object, the amount of chrome to be removed, and the equipment and materials available. Here are some common methods to remove chrome plating:
Specialized Machinery
- Using an Abrasive Blaster
This method involves blasting the chrome-plated surface with abrasive particles, such as sand, glass beads, or steel grit, at high pressure. This can remove the chrome layer as well as any rust or dirt on the metal surface. However, this method can also damage the underlying metal and create a rough texture.
- Using an Ultrasonic Cleaner
This method involves immersing the chrome-plated object in a solution of water and detergent, and then applying ultrasonic waves to create bubbles that scrub the surface. This can loosen and remove the chrome layer as well as any dirt or grease on the metal surface. However, this method may not work well for thick or hard chrome plating.
Chemical Solutions
- Using Hydrochloric Acid
This method involves dipping the chrome-plated object in a solution of hydrochloric acid and water, which can dissolve the chrome layer. However, this method can also corrode the underlying metal and produce toxic fumes.
- Using Sodium Hydroxide
This method involves dipping the chrome-plated object in a solution of sodium hydroxide and water, which can react with the chrome layer and form a soluble salt. However, this method can also damage the underlying metal and produce hazardous waste.
- Perform Reverse Electroplating
This method involves connecting the chrome-plated object to a negative terminal of a power source and immersing it in an electrolytic solution that contains a metal salt. The electric current will cause the chrome layer to detach from the metal substrate and deposit on a positive electrode. However, this method requires special equipment and safety precautions.
Conclusion
Chrome plating is a process that involves electroplating a thin layer of chromium onto a metal object. Chrome plating has various purposes, such as improving the appearance, hardness, corrosion resistance, and friction of the object. Chrome plating can be done using two different methods: hexavalent chromium and trivalent chromium. Hexavalent chromium is a traditional and toxic method, while trivalent chromium is a newer and more environmentally friendly method. Chrome plating can be classified into two main types: decorative chrome plating and hard chrome plating. Decorative chrome plating is used to give a shiny and polished look to the object, while hard chrome plating is used to improve the performance and functionality of the object. Chrome plating can be removed using specialized machinery or chemical solutions, depending on the type and thickness of the chrome layer.